A bond is a form of security that the issuer creates as a way to borrow money. The purchasers are lending money to the issuer by buying a bond, with governments and corporations among those who issue bonds. In return, the purchaser generally receives regular interest payments and can eventually redeem the bond.
Bonds can be purchased outright, but bonds trading is also often carried out via the derivative markets. This means that instruments such as contracts for difference (CFDs) are commonly used when trading bonds.
When bought directly, most bonds are classed as a relatively low-risk and low-return investment. Trading bonds adds volatility, with leverage available to amplify the results of the trade. We’ll be looking at how to start online bond trading and the main features of this market.
Bonds Trading - What It Is and Why Price-Yield Matters
What is bond trading, and why is it so popular? When you trade bonds, you enter a market that’s explained by the following terms.
- Issuer. This is the company, national government or local government that wants to borrow money. Since the issuer is borrowing money and agreeing to pay it back on a certain date, their financial health is crucial to the quality and stability of the bond.
- Investor. The person who buys the bond. The issuer agrees to pay them back the face value, or par value, of the bond. Since bonds can be bought and sold on the secondary market, they don’t need to be held for the full period.
- Coupon rate. This is the interest rate, and it’s paid by the issuer to the investor at the pre-agreed times. The higher risk a bond is, the higher the coupon rate should be to compensate for this.
- Maturity date. The date when the issuer needs to repay the face value to the investor, ending the bond period.
- The yield is the overall return the investor receives on a bond. It’s shown as an annual percentage, taking into account the interest payments received in relation to the price paid.
- Duration is how we measure the effect of interest rate changes on a bond’s price. The more time is left until the maturity date, the greater the effect on its price of any change to the interest rate.
When the price of the bond falls, the yield increases, and it becomes a more attractive investment. This is because the yield is fixed and unaffected by the price.
The risk of default ensures that a higher interest rate is expected on bonds from corporations. Credit spread is a term used to explain the yield difference between a corporate bond and a risk-free treasury yield. It’s calculated as follows: credit spread = corporate bond yield − treasury yield.
How to Trade Bonds Online - Access via CFDs and Futures
There are several ways for retail investors to carry out bonds trading online. CFDs and exchange-traded bond futures both give exposure to the bond’s price movements with no need to hold the bond.
When trading in bonds, you can go long or short, based on whether you think the price will rise or fall. The margin is the cash amount the trader has to maintain in their account.
Credit risk and liquidity risk are the two main concerns for bond investors. By adding leverage, you increase the risk of being liquidated or having a margin call, which is when more money needs to be added to maintain a position that is under threat of being liquidated.
What Markets and Instruments Are Popular for Bonds Trading?
The first decision to make when you want to trade bonds is the type of issuer to choose. Government bond trading is considered lower-risk, since they’re less likely to default. Corporate bonds may issue a higher yield, though.
The key benchmark bonds in each country are based on their sovereign debt. This includes the US treasury notes, the UK’s gilt bond and the various Eurozone government bonds. These are the lowest risk bonds on the market.
Convertible bonds are offered by corporations and are at the higher end of the risk scale. They offer a mixture of income and growth potential, with the opportunity to convert them into the company’s shares. Convertible bond trading covers a mixture of debt and equity that makes it appealing to certain investors.
All of these different bond types can be used for trading purposes. However, you should bear in mind the unique ways each part of the bonds market is affected by price movements and financial news.
Online Bond Trading Strategies - A Simple Framework to Start
When you’re ready to start trading bonds, there are some simple steps to follow that help put you on the right path. This list of steps takes you through the process of choosing bonds and then trading them.
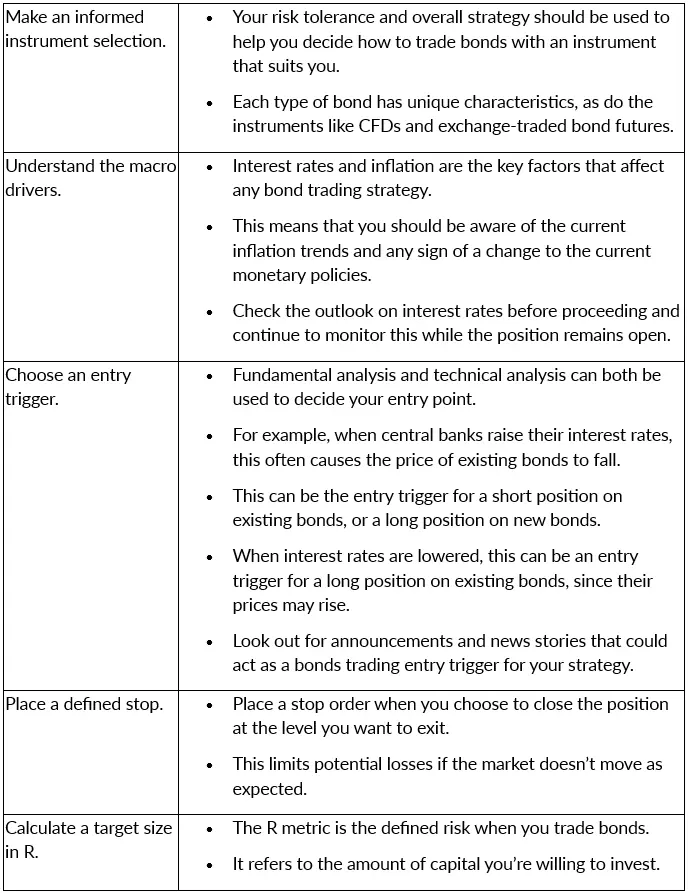
Steps to How to Trade Bonds Online
When you’re ready to start, you should follow the typical flow on bond trading platforms for a smooth performance.
- Choose the market. Find the right bond and instrument for the strategy you have in mind.
- Choose the size of the trade. This is mainly based on your risk tolerance.
- Place the trade. Do this on your chosen online bond trading platform, with a demo account providing the safest approach while you learn the market.
- Monitor the market. Use protective orders, such as a stop-loss, to manage the risk while you monitor.
By choosing a sensible size of trade, you can repeat this process for each new operation while learning each time how to refine your strategy further.
Risks to Know Before You Trade Bonds
Bonds trading involves some risks that you need to take into account. By understanding them, you can also look at the mitigation strategies that you should take into account.
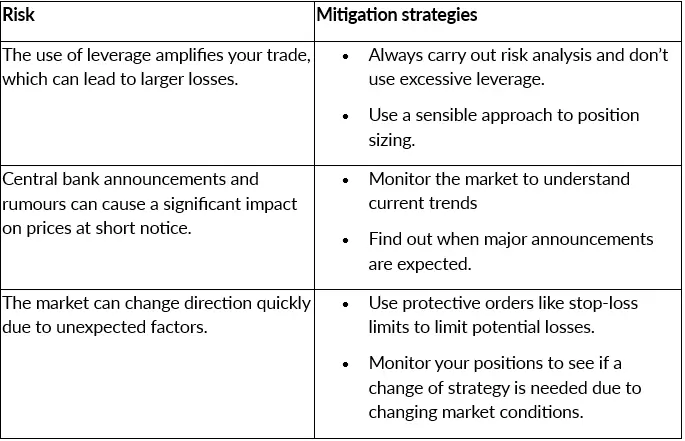
Which Bonds to Trade on ActivTrades
The size of the bond trading market ensures that there are different options you can choose from. To make a strong start, you can check out our Which Bonds to Trade guide. Find detailed information on the most popular benchmarks and see how to access the platform that best fits your needs.
Trading bonds can be carried out using any of the leading platforms we offer: MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, TradingView or ActivTrader.
How to Trade Bonds FAQs
What Are Investment Grade Bonds?
This term is used to describe the bonds that have the highest credit rating on the market. This means that they should carry less risk when you trade them, making them suitable for the majority of bond trading strategies.
What Are High-Yield Bonds, and Are They Suitable for Bond Trading?
These are generally corporate bonds with a lower credit rating and a higher return than government-issued bonds. Corporate bond trading carries more risk but can be part of an effective strategy.
What Are Zero-Coupon Bonds in Trading?
These bonds don’t pay interest, but offer the opportunity to buy them at a discounted rate. They can be traded on a bonds trading platform and are considered to be particularly sensitive to interest rate changes.
How Are Bonds Rated?
Credit rating agencies such as Moody's Investors Service and Fitch Ratings create independent ratings based on their opinion of the creditworthiness of the bond issuer. You should consider the ratings of the bond issuers as part of any bonds trading strategy.
The information provided does not constitute investment research. The material has not been prepared in accordance with the legal requirements designed to promote the independence of investment research and as such is to be considered to be a marketing communication.
All information has been prepared by ActivTrades (“AT”). The information does not contain a record of AT’s prices, or an offer of or solicitation for a transaction in any financial instrument. No representation or warranty is given as to the accuracy or completeness of this information. Demo accounts are for practice purposes only. Performance in a demo environment does not reflect real market conditions and may not be indicative of actual trading results.
Any material provided does not have regard to the specific investment objective and financial situation of any person who may receive it. Past performance is not a reliable indicator of future performance. AT provides an execution-only service. Consequently, any person acting on the information provided does so at their own risk. Forecasts are not guarantees. Rates may change. Political risk is unpredictable. Central bank actions may vary. Platforms’ tools do not guarantee success.